Zenata
Zenata, Morocco’s first eco-city, is a major urban development project located between Casablanca and Rabat. Launched in 2006, it was designed to accommodate 300,000 residents while prioritizing sustainability, social inclusion, and economic opportunity. The city integrates green infrastructure, water conservation systems, and energy-efficient buildings, aiming to set a new benchmark for sustainable urbanization in Africa. Unlike purely commercial developments, Zenata emphasizes affordable housing, mixed-use districts, and job creation, particularly in logistics, education, and healthcare. Its strategic location near Casablanca’s industrial hub strengthens its economic potential. While construction has been gradual, Zenata represents Morocco’s commitment to smart, climate-resilient urban growth, balancing modern infrastructure with environmental and social sustainability in a rapidly urbanizing region.
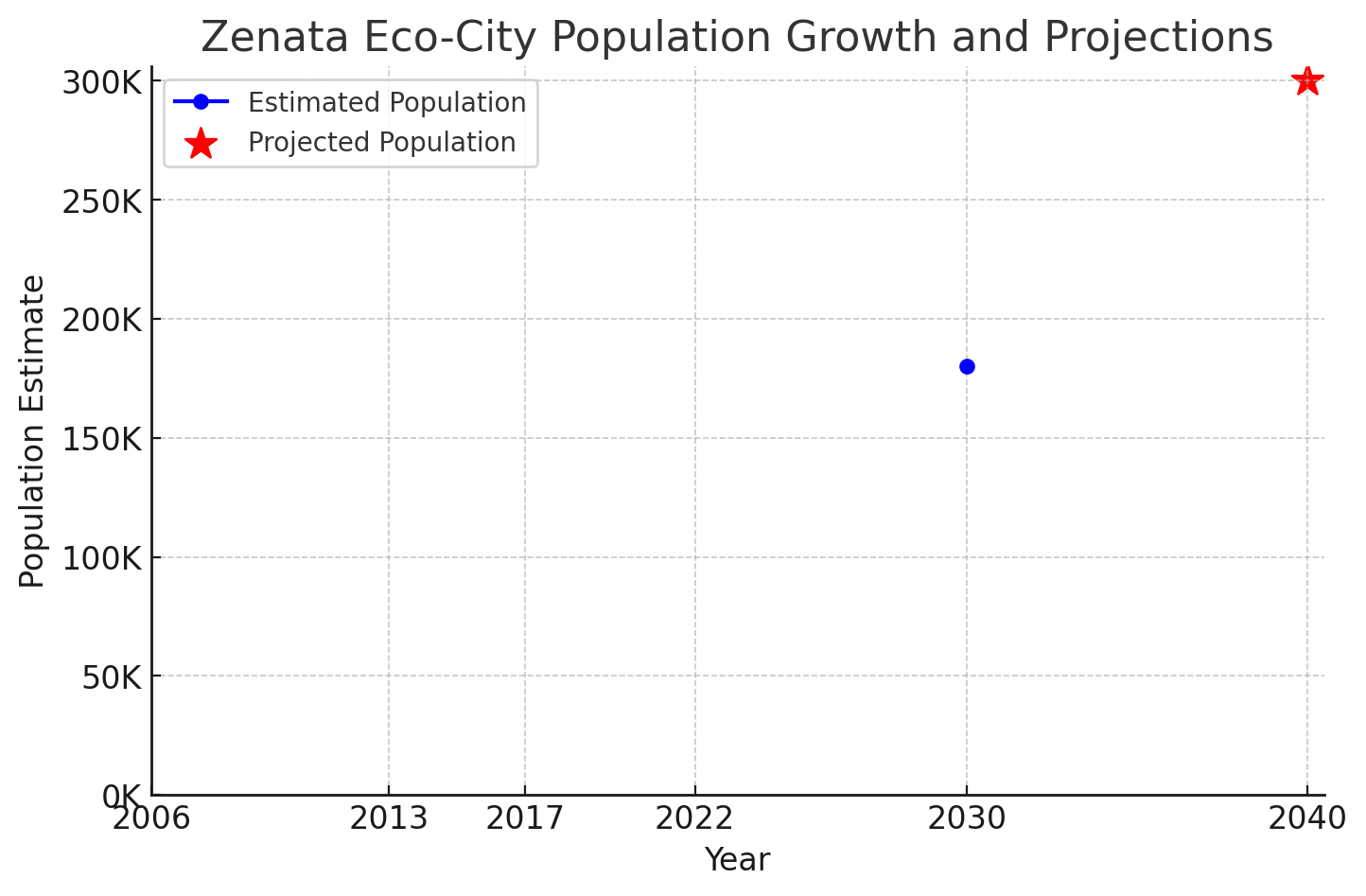
Zenata is a true new city, not just a district, though it remains in the early stages of development. Located between Casablanca and Rabat, Morocco, Zenata was planned as a sustainable eco-city, designed to accommodate 300,000 residents and promote economic growth, environmental resilience, and social inclusivity.
Unlike a district, which would be an extension of an existing city, Zenata is being built from scratch with independent infrastructure, housing, business zones, and public services. It includes green energy systems, water conservation initiatives, and pedestrian-friendly urban planning. However, its population growth has been slow, as relocation efforts and economic incentives are still developing. If fully realized, Zenata will serve as a model for sustainable urbanization in Africa.
Zenata Eco-City has seen slower-than-expected population growth due to challenges in resettlement, phased construction, and economic integration. The relocation of 40,000 residents from informal settlements has been complicated by compensation disputes and eligibility concerns. The city’s development is phased, with infrastructure in place but residential and commercial areas still emerging. Additionally, attracting businesses and residents depends on completing schools, healthcare facilities, and job hubs. While Zenata aims to be Africa’s first sustainable city, its growth is gradual as it balances infrastructure expansion, economic opportunities, and social integration to become a fully functional, livable urban center.
Strengths:
- Designed as Morocco’s First Eco-City – Zenata is planned as a sustainable, mixed-use urban area, prioritizing green infrastructure, energy efficiency, and smart water management.
- Strong Government & Institutional Backing – Led by Morocco’s government and the CDG Group (state investment fund), ensuring long-term commitment.
- Strategic Location – Situated between Casablanca and Rabat, Zenata has the potential to become a key urban and economic hub.
- Some Initial Development Successes – Residential neighborhoods, public spaces, and an IKEA megastore have already been established, signaling early economic activity.
Challenges:
- Slow Population Growth – Despite planning for 300,000 residents, Zenata remains sparsely populated, with many housing units still unoccupied.
- Economic Engine Not Fully Established – While commercial developments have begun, the city lacks strong private-sector anchors outside of retail.
- Competes with Casablanca – Many residents prefer to live in Casablanca, which already has established job markets, making Zenata’s independent growth more difficult.
- Still Feels More Like a Development Project Than a City – Zenata has modern infrastructure, but lacks a true urban vibrancy, similar to other slow-moving planned cities.
Zenata isn’t a failure, but it hasn’t fully taken off as a thriving city either. Its eco-friendly design and government backing give it strong potential, but until industries, businesses, and residents fill in the gaps, it remains an unfinished vision.
| Year | Population Estimate |
|---|---|
| 2006 | Project Initiation |
| 2013 | Infrastructure Development Begins |
| 2017 | Commercial Facilities Operational |
| 2022 | Continued Expansion |
| 2030 | 60% Increase in Households |
| Future | ~300,000 Residents |