Shenzhen

Shenzhen is China’s most successful special economic zone (SEZ) and a global model for rapid urbanization. Once a small fishing village, it transformed into a megacity of over 17 million people in just four decades. Established as an SEZ in 1980, Shenzhen attracted foreign investment, high-tech industries, and manufacturing, becoming China’s Silicon Valley with companies like Huawei, Tencent, and DJI. Its urban form prioritizes dense, mixed-use development, advanced public transit, and innovation hubs like Qianhai and Futian. While Shenzhen leads in technology, finance, and sustainability, challenges include high housing costs, migrant worker integration, and environmental pressures. The city is now focusing on high-tech R&D, green development, and global connectivity, reinforcing its status as a leader in urban and economic innovation.
Shenzhen is a new city, though it has evolved over time. Originally a small fishing village, it was designated as China’s first Special Economic Zone (SEZ) in 1980, which spurred its transformation into a major urban center. While it started as a small town, Shenzhen grew rapidly into a metropolitan city, attracting domestic and international businesses, particularly in technology, manufacturing, and finance.
Shenzhen is now one of China’s largest cities, with a population of over 17 million people. It has its own municipal government and is not part of any other city’s administrative structure. Though initially a district within Guangdong Province, Shenzhen is a distinct, self-sustaining city and one of China’s most dynamic urban centers.
Shenzhen is one of the most successful planned urban experiments in history, transforming into a global financial, technological, and manufacturing hub. While it has some challenges typical of fast-growing megacities, its scale of success, innovation, and urban vibrancy are virtually unmatched.
Strengths:
- Rapid Growth and Transformation: Shenzhen rose from a small fishing village to a global metropolis of over 17 million people in just a few decades.
- Economic Powerhouse: As one of China’s first Special Economic Zones, Shenzhen became a magnet for foreign investment, manufacturing, and innovation. Today, it’s home to global tech giants like Huawei, Tencent, and DJI.
- Cutting-Edge Infrastructure: The city boasts world-class public transport, green spaces, a high-speed rail hub, and a modern skyline that rivals those of established global cities.
- Innovative Urban Planning: Shenzhen is known for mixed-use developments, sustainable urban initiatives, and continuous redevelopment to maintain competitiveness.
- Global Tech and Innovation Hub: Shenzhen’s combination of hardware manufacturing prowess, startup culture, and research and development makes it one of the world’s most dynamic innovation ecosystems.
Challenges:
- Housing Affordability and Density: As a fast-growing city, Shenzhen faces significant challenges related to housing costs, income inequality, and high population density.
- Environmental Pressure: While it has implemented numerous green initiatives, the city still grapples with pollution and ecological sustainability issues due to rapid industrialization.
- Dependence on Manufacturing and Tech: Shenzhen’s success is tightly linked to the tech and manufacturing sectors, which can leave it vulnerable to global economic fluctuations and trade tensions.
| Year | Event | Population Estimate |
|---|---|---|
| 1980 | Establishment of Shenzhen Special Economic Zone | ~30,000 |
| 1990 | Rapid industrial growth and urbanization | ~2,019,400 |
| 2000 | Continued expansion and development | ~4,333,000 |
| 2010 | Emergence as a major global city | ~10,357,938 |
| 2020 | Population reaches new heights | ~17,560,000 |
| 2025 | Projected population | ~20,000,000 |
| 2035 | Projected population | ~22,000,000 |
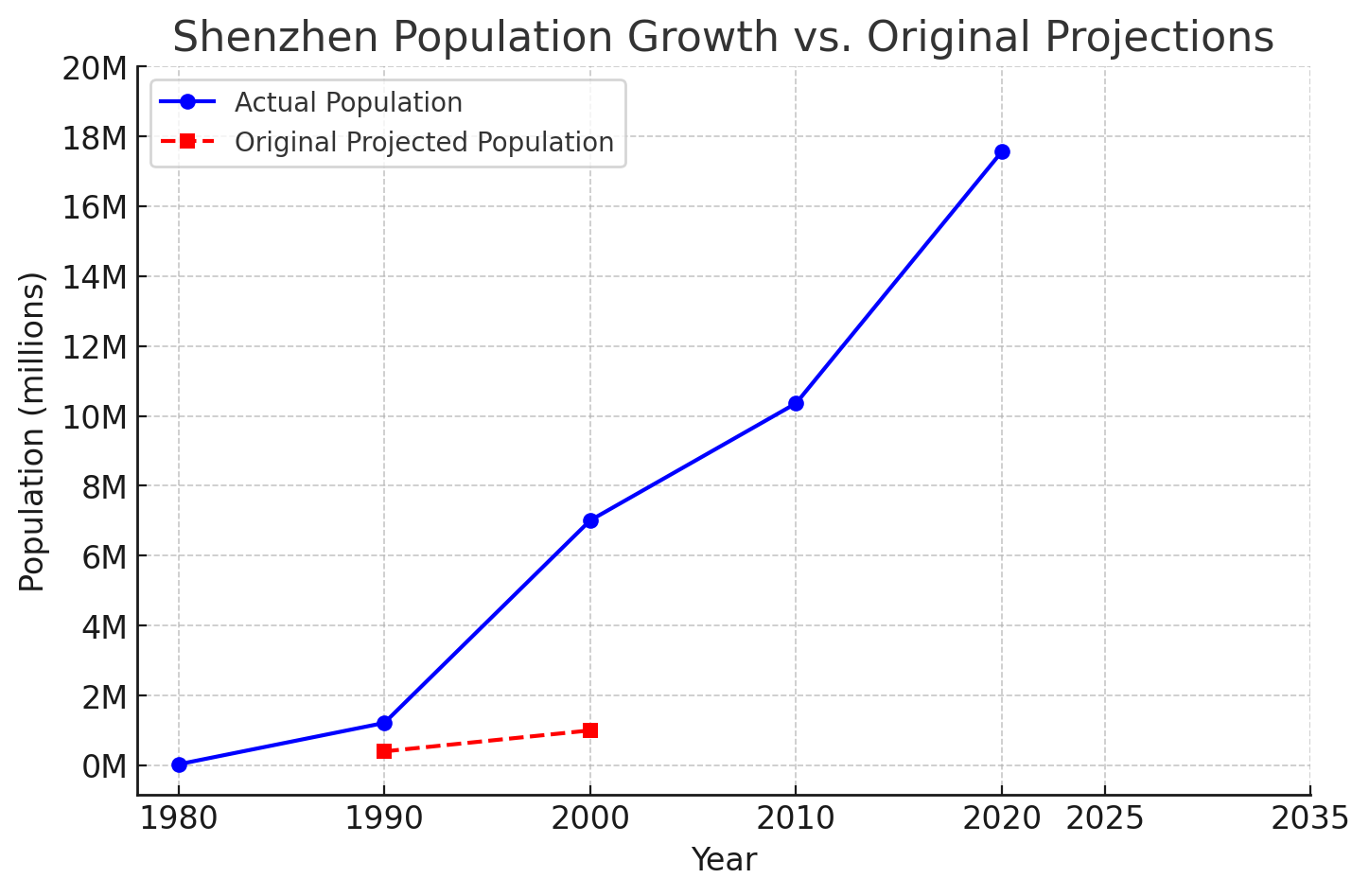
Original population projections for the city:
| Year | Projected Population | Actual Population |
|---|---|---|
| 1990 | 400,000 | 1,214,000 |
| 2000 | 1,000,000 | 7,008,000 |
| 2006 | N/A | 8,460,000 |