Konza Technopolis
Konza Technopolis, Kenya’s flagship smart city, is a high-tech innovation hub located 60 km south of Nairobi. Launched in 2008 under Kenya Vision 2030, the project aims to position the country as a leading digital economy in Africa. Originally conceived to address Kenya's growing tech ecosystem and attract global firms, Konza is planned as a mixed-use city, featuring technology parks, research institutions, business districts, and residential areas. It focuses on fostering industries like IT, biotech, and advanced manufacturing.
The first phase includes the Konza Data Center, smart infrastructure, and innovation labs, but progress has been slower than expected due to funding delays and private sector hesitancy. Despite this, the city remains a promising model for tech-driven urban development, and with continued government support, investment in fiber networks, and green energy, it continues to attract both global firms and startups.
Konza Technopolis is a new city, not just a district. Located in Machakos County, about 60 kilometers south of Nairobi, Kenya, it is being developed as a high-tech urban hub with a focus on innovation, technology, and sustainability. The city is part of Kenya’s Vision 2030 and is designed to be a self-sustaining, smart city with residential, commercial, and industrial zones.
Konza aims to attract global tech companies, startups, and research institutions, with infrastructure planned for smart services, green energy, and high-speed connectivity. Unlike a district, which is an extension of an existing city, Konza Technopolis is being developed from the ground up, making it a new city intended to serve as Kenya’s technology and innovation hub.
Konza Technopolis embodies Kenya's aspirations to become a leading technology and innovation hub in Africa. While foundational infrastructure and international partnerships signal potential, the project faces ongoing challenges related to delays, occupancy, and competition. Sustained efforts in addressing these issues are crucial for Konza to transition from a visionary project to a thriving urban and economic center.
Strengths:
- Strategic Vision: Konza Technopolis is a flagship project under Kenya's Vision 2030, aiming to establish a world-class technology hub and smart city.
- Infrastructure Development: Key facilities like the National Data Centre and the Konza Complex headquarters have been completed, providing a foundation for future growth.
- International Partnerships: Collaborations, such as the financing agreement with the Republic of Korea for the development of a Digital Media City, highlight global interest and investment.
- Educational Initiatives: The establishment of the Kenya Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (Kenya-KAIST) within Konza aims to foster research and innovation, contributing to the city's knowledge base.
Challenges:
- Delayed Timelines: Since its inception in 2008, Konza has faced significant delays, with initial projections unmet and construction progress slower than anticipated.
- Population and Occupancy: Designed to host 200,000 residents, the city has yet to attract a substantial population, with many facilities remaining underutilized.
- Funding and Bureaucracy: Grand plans have been hindered by bureaucratic red tape and funding challenges, impacting investor confidence and project momentum.
- Competition from Other Hubs: Emerging tech hubs in other African countries present competitive challenges, potentially diverting investment and talent away from Konza.
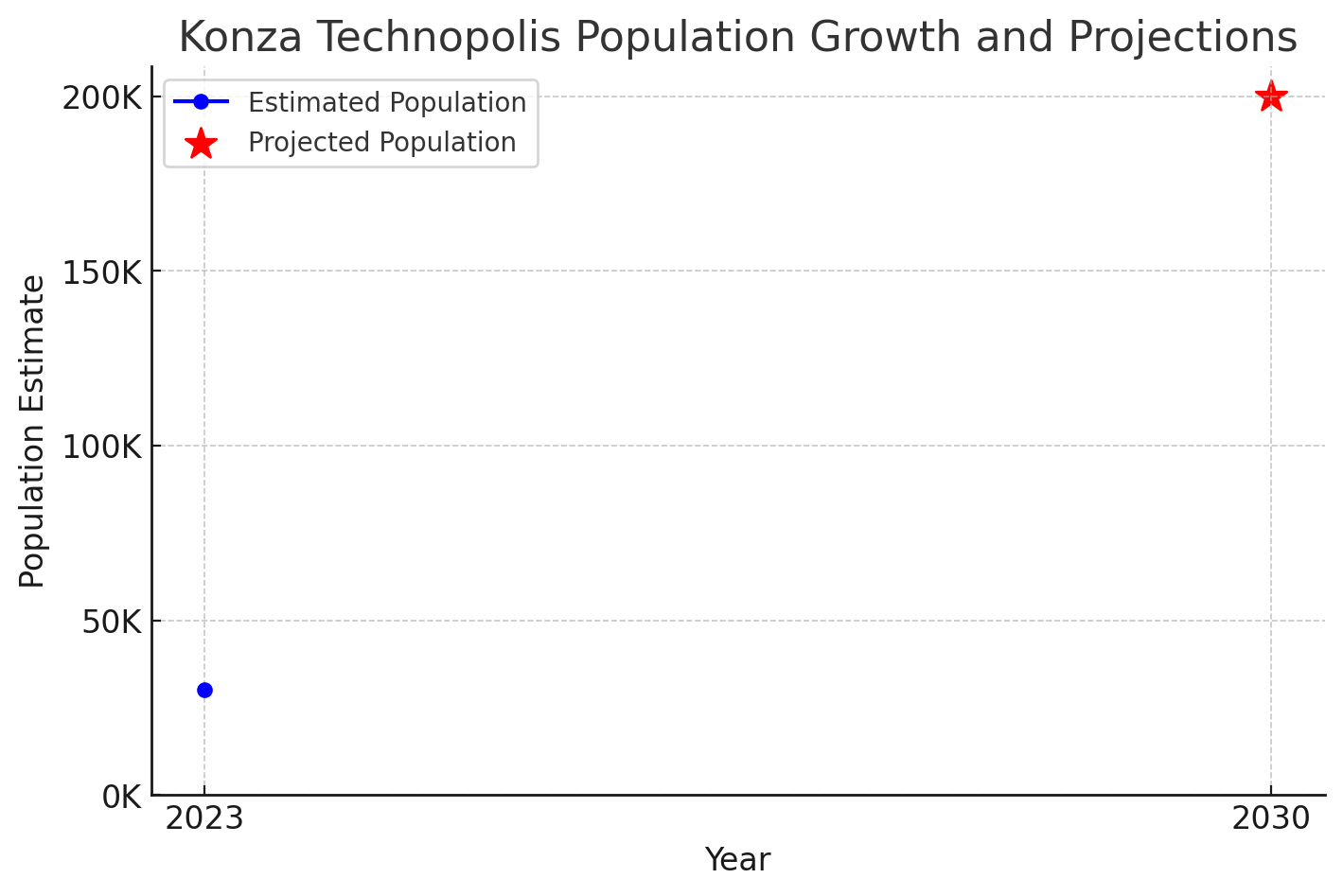
The development of Konza Technopolis is structured in multiple phases, with specific population and employment targets:
- Phase 1: Projected to host over 30,000 residents and create approximately 17,000 jobs upon completion.
- Full Build-Out: Aims to accommodate a population exceeding 200,000 residents, supported by a workforce of around 200,000, by the year 2030.
| Year | Population Estimate |
|---|---|
| 2023 | >30,000 |
| 2030 | >200,000 |